Czochralski Crystal Growth
Galaxy Compound Semiconductors, Inc. uses the Czochralski crystal growth method for single crystal GaSb and InSb boule production.
Overview of the Czochralski Method:
This method yields large crystals with low defect concentrations and is especially well suited for volatile component single crystal growth such as the antimonides. For GaSb and InSb boule production, Galaxy fabricates their own seeds and employs conventional seed rotation and translation capabilities in the manufacturing process. Specific system temperature gradients and pull rates are a function of the end product compound and boule size.
Czochralski Boule size from Galaxy:
Galaxy routinely grows GaSb crystals ranging from 2" (50mm) to 100mm (4") in diameter and InSb crystal boules ranging from 2" (50mm) to 125mm (5") in diameter. Larger format 150mm (6") InSb boule growth has been successfully demonstrated and is available upon special request
Galaxy's Czochralski process:
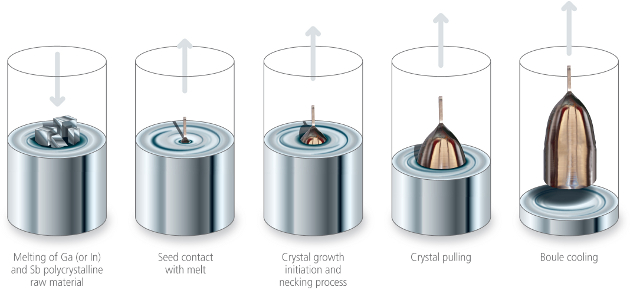
Galaxy begins with the highest purity Gallium, Indium and Antimony. The materials (in either elemental or pre-synthesized forms) are placed in the growth crucible of the Czochralski puller system, along with tellurium as the dopant; amounts of Te are based on the desired crystal doping level. An inert atmosphere is implemented and the quartz crucible is heated until the melting and compound synthesis of the material occurs. During the Czochralski method, the InSb/GaSb seed crystal is rotated and slowly withdrawn from the melt, forming the initial boule growth. By consistently controlling the temperature gradients, rate of crystal pulling and rotation rates, extracting a large, single-crystal, cylindrical boule is achieved. The final boule diameter and length is a function of the starting crucible size, weight of the melt and total process time. The boule must be slowly cooled in order to prevent crystal dislocation defects/slips and cracking.

 Galaxy Compound Semiconductors Inc.
Galaxy Compound Semiconductors Inc.